-
Biweekly 27
-
Biweekly 28
Showing posts with label leetcode. Show all posts
Showing posts with label leetcode. Show all posts
Monday, June 22, 2020
Leetcode Biweekly 27, 28
Thursday, June 13, 2019
leetcode - dp - 902. Numbers At Most N Given Digit Set
902. Numbers At Most N Given Digit Set
- Given an character set D, which contains only digits '1'-'9' in sorted order
- Given an integer N
- Count number of integers consisting of D, less than or equal to N
Better code:
CY, first attempt
int solve(const vector<int>& nums, const vector<int>& digs, int exp10, const vector<int>& power10s) { const int n = digs.size(); int ans = 0; for (int i = exp10; i >= 0; --i) { int idx = 0; for (; idx < n; ++idx) if (digs[idx] > nums[i]) break; if (!idx) break; int cnt = power10s[i]; if (digs[idx - 1] == nums[i] && i > 0) ans += (idx - 1) * cnt; else { ans += idx * cnt; break; } } return ans; } int atMostNGivenDigitSet(vector<string>& D, int N) { // 2123: 0 ~ 999 + 1000 ~ 1999 + 2000 ~ 2123 // {1, 2, 3, 4} // 2567: 0 ~ 999 + 1000 ~ 1999 + 2000 ~ 2567 int exp10 = 0; int64_t power10; for (power10 = 10; power10 <= N; power10 *= 10) ++exp10; const int n = D.size(); int ans = 0; vector<int> digs; digs.reserve(n); for (const auto &d : D) digs.push_back(stoi(d)); vector<int> nums; nums.reserve(exp10 + 1); int NN = N; while (NN != 0) { nums.push_back(NN % 10); NN /= 10; } vector<int> power10s; power10s.reserve(exp10+1); int cnt = 1; power10s.push_back(1); for (int j = 0; j < exp10; ++j) { cnt *= n; ans += cnt; power10s.push_back(cnt); } if (nums[exp10] < digs[0]) return ans; return ans + solve(nums, digs, exp10, power10s); }
leetcode - knapsack dp - 1049. Last Stone Weight II
1049. Last Stone Weight II (weekly 137)
- Given an integer (stone) array, separate the integers into two sets, named A, B
- return the minimum value of Sum(A) - Sum(B)
Note:
- 1 <= stones.length <= 30
- 1 <= stones[i] <= 100
Reference from committed code.
Very smart.
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) { constexpr int MAX = 3000 / 2 + 100 + 1; bitset<MAX> possibleSum; possibleSum[0] = true; for (int s : stones) possibleSum = possibleSum | (possibleSum << s); int total = accumulate(stones.begin(), stones.end(), 0); // find left partition. int leftPart = 0; for (int i = total / 2; i >= 0; --i) if (possibleSum[i]) { leftPart = i; break; } // find right partition. int rightPart = 0; for (int i = (total + 1) / 2; i <= total; ++i) if (possibleSum[i]) { rightPart = i; break; } return rightPart - leftPart; }
by neal_wu's contest solution.
int lastStoneWeightII(vector<int>& stones) { int n = stones.size(); vector<bool> possible(2 * MAX + 1, false); possible[MAX] = true; for (int stone : stones) { vector<bool> next_possible(2 * MAX + 1, false); for (int x = 0; x <= 2 * MAX; x++) if (possible[x]) next_possible[x + stone] = next_possible[x - stone] = true; possible = next_possible; } for (int i = 0; i <= MAX; i++) if (possible[MAX + i]) return i; return -1; }
Tuesday, June 11, 2019
leetcode weekly 132 to 136 - other problems
1074. Number of Submatrices That Sum to Target
Submatrices Sum.
Submatrices Sum.
// CY first attempt (5728 ms, 48.58%, 13 MB, 100%) int numSubmatrixSumTarget(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) { const int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(); vector<int> prefSum(m + 1); vector<int> rowSum(m); int total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { fill(rowSum.begin(), rowSum.end(), 0); for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) { for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) rowSum[k] += matrix[k][j]; for (int k = 1; k <= m; ++k) prefSum[k] = prefSum[k - 1] + rowSum[k - 1]; for (int k1 = 0; k1 < m; ++k1) for (int k2 = k1 + 1; k2 <= m; ++k2) if (prefSum[k2] - prefSum[k1] == target) ++total; } } return total; }
leetcode - knapsack dp
956. Tallest Billboard
(a) [1,2], max sum = 0.
(b) [1,2,3,4,5,6], max sum = 10, can separate into {2, 3, 5} and {4, 6}
12 ms version, sampled from committed solution:
- Given an integer array, separate these numbers (don't have to use all numbers) into 2 sets, named A and B.
- Sum(A) = Sum(B)
- Find the maximum sum.
Note: The sum of rods is at most 5000.
Example:
(a) [1,2], max sum = 0.
(b) [1,2,3,4,5,6], max sum = 10, can separate into {2, 3, 5} and {4, 6}
12 ms version, sampled from committed solution:
// left/right is billboard height of each side // index points to next rod void dfs_12ms(vector<int> &rods, int left, int right, int remain, int index, int &result) { if (abs(left - right) > remain || left + right + remain <= result * 2) return; if (left == right && result < left) result = left; if (index == rods.size()) return; remain -= rods[index]; dfs_12ms(rods, left + rods[index], right, remain, index + 1, result); dfs_12ms(rods, left, right + rods[index], remain, index + 1, result); dfs_12ms(rods, left, right, remain, index + 1, result); } int tallestBillboard_12ms(vector<int> &rods) { sort(rods.begin(), rods.end(), greater<int>()); int sum = 0; for (const auto &r : rods) sum += r; int result = 0; dfs_12ms(rods, 0, 0, sum, 0, result); return result; }
// ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/tallest-billboard/discuss/203274/Simple-C%2B%2B-DP-beating-100-O(NM)#_=_ // 28 ms (CY 2nd attempt) bool isValid(int s) const { return s >= 0; } int tallestBillboard(vector<int>& rods) { if (rods.empty()) return 0; int maxsum = accumulate(rods.begin(), rods.end(), 0) / 2; const int n = rods.size(); // dp[i][diff]: The maximum pair of s0 and s1 from // set of {rods[j], j <= i} which has difference = diff // // s1 is always s0, so dp[i][diff] = s0 + diff = s1 //vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(maxsum + 1)); int dpPrevData[maxsum + 1]; int dpCurData[maxsum + 1]; int *dpPrev = dpPrevData; int *dpCur = dpCurData; for (int i = 1; i <= maxsum; i++) dpPrev[i] = -1; dpPrev[0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { int rodi = rods[i - 1]; for (int j = 0; j <= maxsum; ++j) { /// case a: Do not use rodi. int a = dpPrev[j]; /// case b: Add rodi to s1. int b = -1; if (j >= rodi && isValid(dpPrev[j - rodi])) b = dpPrev[j - rodi] + rodi; /// case c: Add rodi to s0, but s1 is still greater than s0. int c = -1; if (j + rodi <= maxsum) // rodi > j ) c = dpPrev[j + rodi]; /// case d: Add rodi to s0, but s0 is now greater than s1, /// and will be swapped. int d = -1; if (rodi > j && rodi - j <= maxsum && isValid(dpPrev[rodi - j])) d = dpPrev[rodi - j] + j; dpCur[j] = max({a, b, c, d}); } swap(dpCur, dpPrev); } return dpPrev[0]; }
Thursday, June 6, 2019
leetcode weekly 132 to 136 - overview
weekly 136
(not really easy..) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-136/problems/robot-bounded-in-circle/
(graph coloring) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-136/problems/flower-planting-with-no-adjacent/
(hard)(suffix-tree)(lcp) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-136/problems/longest-duplicate-substring/
weekly 135
(tree traverse) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-135/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
(sliding window)(good) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-135/problems/moving-stones-until-consecutive-ii/
weekly 134
(move stone) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-134/problems/moving-stones-until-consecutive/
(dp)(classical)(lcs) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-134/problems/uncrossed-lines/
weekly 133
(good)(partial sort) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-133/problems/two-city-scheduling/
(good)(array) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-133/problems/maximum-sum-of-two-non-overlapping-subarrays/
(good)(hard)(streamer)(ref cui’s sol) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-133/problems/stream-of-characters/
weekly 132
(not really easy..) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-132/problems/divisor-game/
(tree-inorder) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-132/problems/maximum-difference-between-node-and-ancestor/
(not really hard) https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-132/problems/recover-a-tree-from-preorder-traversal/leetcode weekly 132 to 136 - dp problems
weekly 132
(dp) 1027. Longest Arithmetic Sequence
Given an array A of integers, return the length of the longest arithmetic subsequence in A.
e.g. [20,1,15,3,10,5,8] = 4, [20,15,10,5] is the longest arithmetic subsequence.
ref: lee215' [Java/C++/Python] DP
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-arithmetic-sequence/discuss/274611/JavaC%2B%2BPython-DP
weekly 134
(dp)(classical)(lcs) 1035. Uncrossed Lines
Given two integer arrays A and B.
We can draw a connecting line to connect two numbers from A, B if:
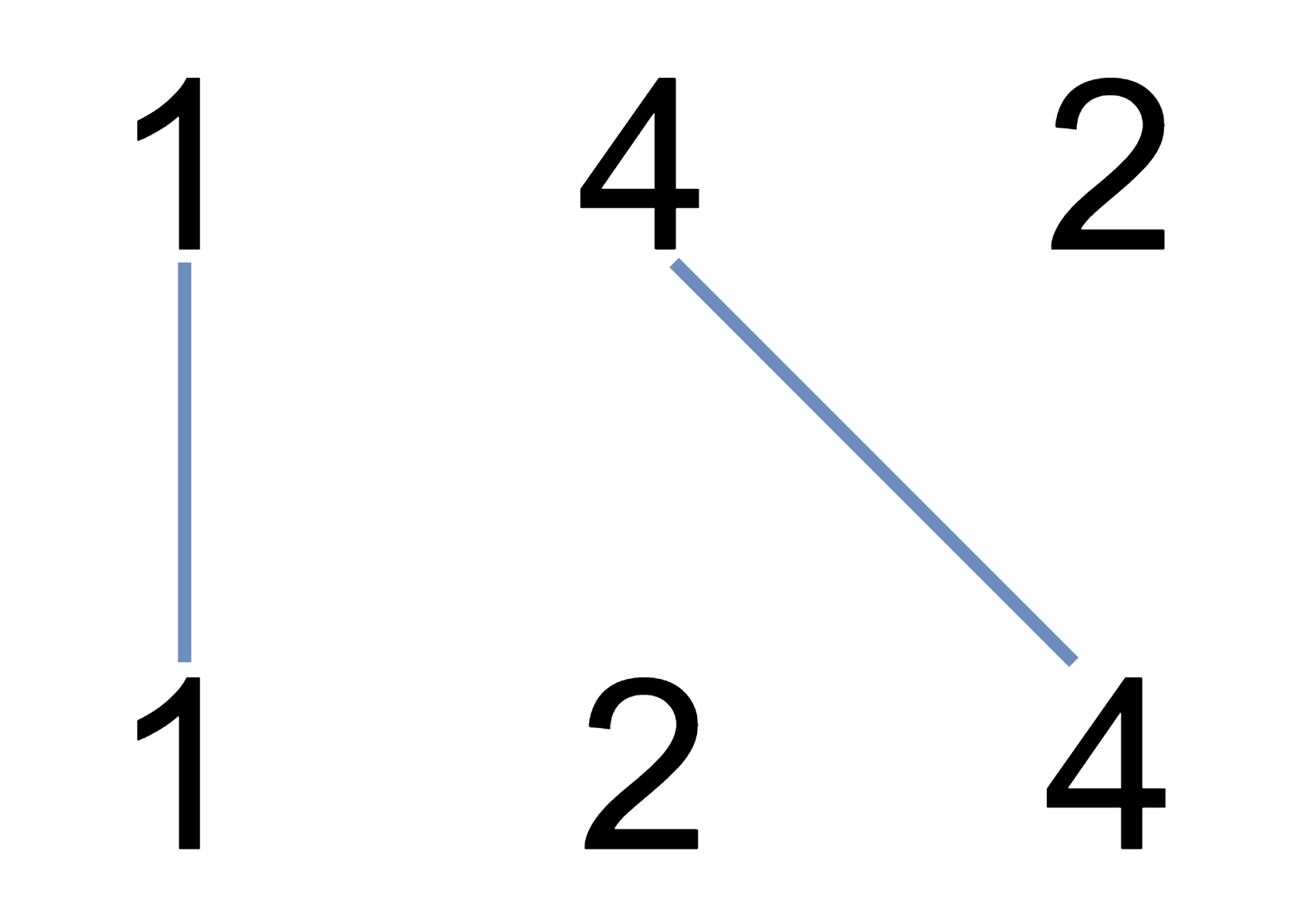
Return the maximum connecting line.
weekly 135
(dp)(good) 1039. Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon
Given a n-sided convex with vertices A[0], A[1], ... A[n - 1]
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-score-triangulation-of-polygon/discuss/286753/C%2B%2B-with-picture
weekly 136
(dp) 1043. Partition Array for Maximum Sum
Example
(dp) 1027. Longest Arithmetic Sequence
Given an array A of integers, return the length of the longest arithmetic subsequence in A.
e.g. [20,1,15,3,10,5,8] = 4, [20,15,10,5] is the longest arithmetic subsequence.
ref: lee215' [Java/C++/Python] DP
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-arithmetic-sequence/discuss/274611/JavaC%2B%2BPython-DP
// (CY 2nd attempt.) 2016 ms, faster than 51.45% // Memory Usage: 365.3 MB, less than 28.94% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { const int n = A.size(); // dp[i] = <Diff, Length> information start from A[0], and end with A[i] // // dp[i][diff] = arithmetic sequence length for 'diff', // start from A[0], and end with A[i] // // Update order: // for i = 0..n-1 // for j = i+1..n-1 // dp[j][diff] = dp[i][diff] + 1 vector<unordered_map<int, int>> dp(n); int longest = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { const int d = A[j] - A[i]; const int cnt = dp[i][d] + 1; dp[j][d] = cnt; longest = max(longest, cnt); } } return longest + 1; }
// From Sampled commit - Without unordered_map // 2380 ms, faster than 36.17% // Memory Usage: 8.7 MB, less than 92.28% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { int count = 2; int ans = 2; for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < A.size(); j++) { int diff = A[j] - A[i]; int target = A[j] + diff; count = 2; for (int k = j+1; k < A.size(); k++) { if (A[k] == target){ target += diff; count++; ans = max(ans, count); } } } } return ans; }
// From Sampled commit // 24 ms, faster than 99.88% // 26.5 MB, less than 80.83% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { int n = A.size(); int pos[10001]; memset(pos,-1,sizeof(pos)); int d[n][n]; memset(d,0,sizeof(d)); int ret = 0; pos[A[0]] = 0; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { for(int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { int prev = 2*A[i] - A[j]; if (prev < 0 || prev > 10000 || pos[prev] == -1) continue; d[i][j] = d[pos[prev]][i] + 1; if (d[i][j] > ret) ret = d[i][j]; } pos[A[i]] = i; } return ret + 2; }
weekly 134
(dp)(classical)(lcs) 1035. Uncrossed Lines
Given two integer arrays A and B.
We can draw a connecting line to connect two numbers from A, B if:
- A[i] == B[j]
- The line doesn't intersect with other connecting line.
- Each number can only belong to to one connecting line.

Return the maximum connecting line.
int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) { // Longest Common Subsequence. const int m = A.size() + 1; const int n = B.size() + 1; vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n)); for (int r = 1; r < m; ++r) for (int c = 1; c < n; ++c) if (A[r-1] == B[c-1]) dp[r][c] = dp[r - 1][c - 1] + 1; else dp[r][c] = max(dp[r - 1][c], dp[r][c - 1]); return dp[m - 1][n - 1]; }
weekly 135
(dp)(good) 1039. Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon
Given a n-sided convex with vertices A[0], A[1], ... A[n - 1]
- Triangulate it into n - 2 triangles
- Each triangle has a score = A[i] * A[j] * A[k], i, j, k is the vertex of triangle.
- Return the smallest total score
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-score-triangulation-of-polygon/discuss/286753/C%2B%2B-with-picture
// ref: neal_wu's contest solution vector<vector<int>> dp; int n; int next(int idx) const { return (idx + 1) % n; } int solve(int begin, int end, const vector<int> &A) { if (next(begin) == end) return 0; if (dp[begin][end]) return dp[begin][end]; int best = INT_MAX; for (int i = next(begin); i != end; i = next(i)) best = min(best, A[begin]*A[i]*A[end] + solve(begin, i, A) + solve(i, end, A)); dp[begin][end] = best; return best; } int minScoreTriangulation(vector<int>& A) { n = A.size(); dp.resize(n, vector<int>(n)); int best = INT_MAX; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) best = min(best, solve(i, j, A) + solve(j, k, A) + solve(k, i, A) + A[i] * A[j] * A[k]); return best; }
weekly 136
(dp) 1043. Partition Array for Maximum Sum
Example
Input: A = [1,15,7,9,2,5,10], K = 3 Output: 84 Explanation: A becomes [15,15,15,9,10,10,10]
Return the largest sum of the given array after partitioning.
int maxSumAfterPartitioning(vector<int>& A, int K) { // From lee215: // dp[i] record the maximum sum we can get considering A[0] ~ A[i] // // To get dp[i], we will try to change k last numbers separately to // the maximum of them, where k = 1 to k = K. const int n = A.size(); int dp[n]; dp[0] = A[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { int maxSum = 0; int maxElem = 0; for (int j = 0; j < K; ++j) { if (i - j < 0) continue; maxElem = max(maxElem, A[i - j]); int curSum = maxElem * (j + 1); if (i - j - 1 >= 0) curSum += dp[i - j - 1]; maxSum = max(maxSum, curSum); } dp[i] = maxSum; } return dp[n - 1]; }
// By neal_wu's contest solution int maxSumAfterPartitioning(vector<int>& A, int K) { int N = A.size(); vector<int> dp(N + 1, 0); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { int most = 0; for (int j = i - 1; j >= max(i - K, 0); j--) { most = max(most, A[j]); dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + (i - j) * most); } } return dp[N]; }
Sunday, March 10, 2019
Saturday, March 9, 2019
leetcode contest 124
#1369
995. Minimum Number of K Consecutive Bit Flips
By lee215.
995. Minimum Number of K Consecutive Bit Flips
In an array
A containing only 0s and 1s, a K-bit flip consists of choosing a (contiguous) subarray of length K and simultaneously changing every 0 in the subarray to 1, and every 1 in the subarray to 0.
Return the minimum number of
K-bit flips required so that there is no 0 in the array. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: A = [0,1,0], K = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: Flip A[0], then flip A[2].
Example 2:
Input: A = [1,1,0], K = 2 Output: -1 Explanation: No matter how we flip subarrays of size 2, we can't make the array become [1,1,1].
Example 3:
Input: A = [0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0], K = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: Flip A[0],A[1],A[2]: A becomes [1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0] Flip A[4],A[5],A[6]: A becomes [1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0] Flip A[5],A[6],A[7]: A becomes [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 300001 <= K <= A.length
By lee215.
// ref. lee215's solution int minKBitFlips(vector<int>& A, int K) { const int n = A.size(); vector<bool> IsFlipped(n, false); bool Flipped = false; int Ans = 0; // 00010110 K = 3 // => 11110110 Flipped = true // => 11111000 // => 11111111 // 01010110 K = 3 // => 10110110 Flipped = true // => 11000110 Flipped = false // => 11111110 Flipped = true for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (i >= K) Flipped ^= IsFlipped[i - K]; if ((bool)A[i] == Flipped) { if (i + K > n) return -1; IsFlipped[i] = true; Flipped = !Flipped; ++Ans; } } return Ans; }
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)