(dp) 1027. Longest Arithmetic Sequence
Given an array A of integers, return the length of the longest arithmetic subsequence in A.
e.g. [20,1,15,3,10,5,8] = 4, [20,15,10,5] is the longest arithmetic subsequence.
ref: lee215' [Java/C++/Python] DP
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-arithmetic-sequence/discuss/274611/JavaC%2B%2BPython-DP
// (CY 2nd attempt.) 2016 ms, faster than 51.45% // Memory Usage: 365.3 MB, less than 28.94% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { const int n = A.size(); // dp[i] = <Diff, Length> information start from A[0], and end with A[i] // // dp[i][diff] = arithmetic sequence length for 'diff', // start from A[0], and end with A[i] // // Update order: // for i = 0..n-1 // for j = i+1..n-1 // dp[j][diff] = dp[i][diff] + 1 vector<unordered_map<int, int>> dp(n); int longest = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { const int d = A[j] - A[i]; const int cnt = dp[i][d] + 1; dp[j][d] = cnt; longest = max(longest, cnt); } } return longest + 1; }
// From Sampled commit - Without unordered_map // 2380 ms, faster than 36.17% // Memory Usage: 8.7 MB, less than 92.28% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { int count = 2; int ans = 2; for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < A.size(); j++) { int diff = A[j] - A[i]; int target = A[j] + diff; count = 2; for (int k = j+1; k < A.size(); k++) { if (A[k] == target){ target += diff; count++; ans = max(ans, count); } } } } return ans; }
// From Sampled commit // 24 ms, faster than 99.88% // 26.5 MB, less than 80.83% int longestArithSeqLength(vector<int>& A) { int n = A.size(); int pos[10001]; memset(pos,-1,sizeof(pos)); int d[n][n]; memset(d,0,sizeof(d)); int ret = 0; pos[A[0]] = 0; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { for(int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { int prev = 2*A[i] - A[j]; if (prev < 0 || prev > 10000 || pos[prev] == -1) continue; d[i][j] = d[pos[prev]][i] + 1; if (d[i][j] > ret) ret = d[i][j]; } pos[A[i]] = i; } return ret + 2; }
weekly 134
(dp)(classical)(lcs) 1035. Uncrossed Lines
Given two integer arrays A and B.
We can draw a connecting line to connect two numbers from A, B if:
- A[i] == B[j]
- The line doesn't intersect with other connecting line.
- Each number can only belong to to one connecting line.
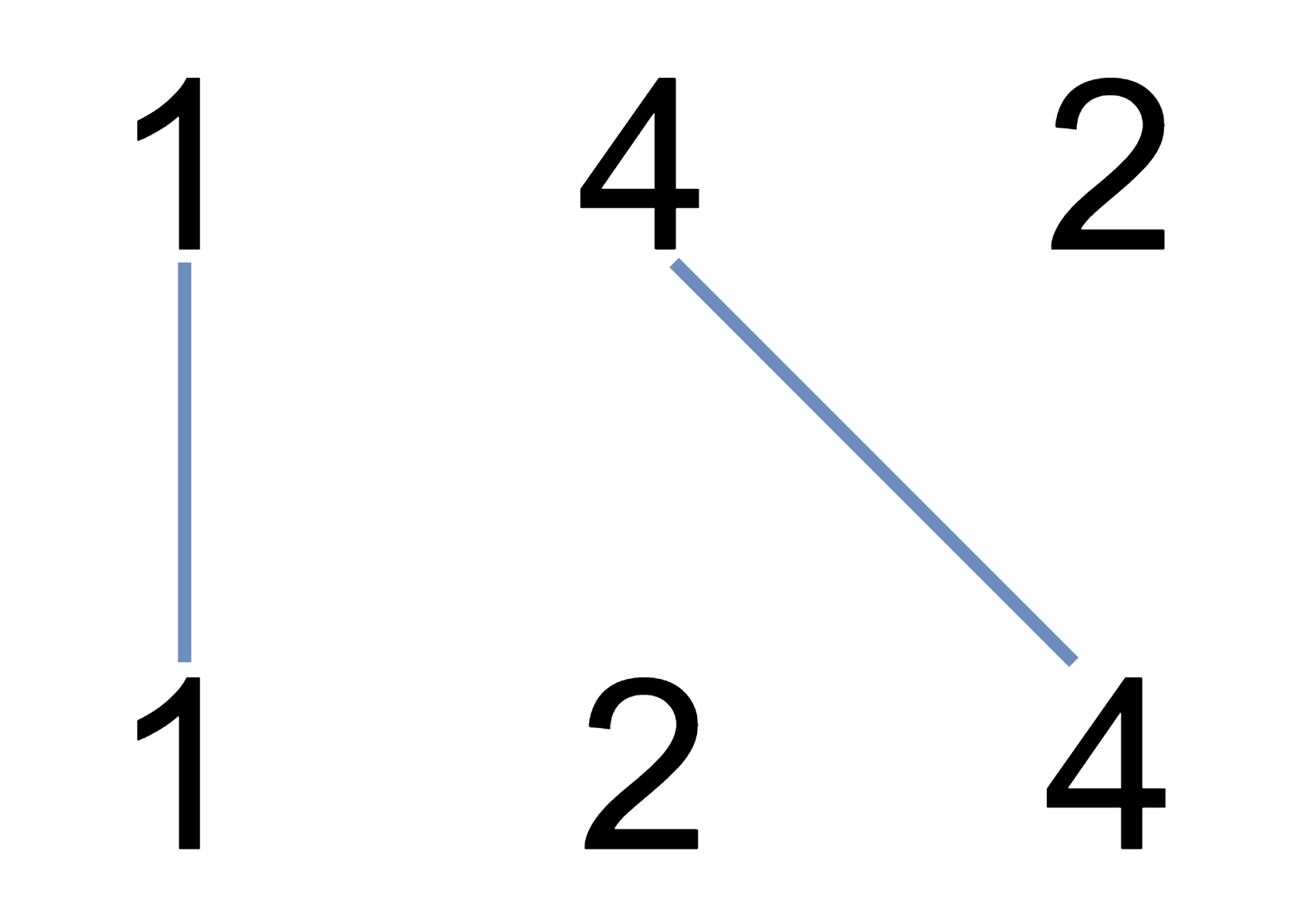
Return the maximum connecting line.
int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) { // Longest Common Subsequence. const int m = A.size() + 1; const int n = B.size() + 1; vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n)); for (int r = 1; r < m; ++r) for (int c = 1; c < n; ++c) if (A[r-1] == B[c-1]) dp[r][c] = dp[r - 1][c - 1] + 1; else dp[r][c] = max(dp[r - 1][c], dp[r][c - 1]); return dp[m - 1][n - 1]; }
weekly 135
(dp)(good) 1039. Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon
Given a n-sided convex with vertices A[0], A[1], ... A[n - 1]
- Triangulate it into n - 2 triangles
- Each triangle has a score = A[i] * A[j] * A[k], i, j, k is the vertex of triangle.
- Return the smallest total score
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-score-triangulation-of-polygon/discuss/286753/C%2B%2B-with-picture
// ref: neal_wu's contest solution vector<vector<int>> dp; int n; int next(int idx) const { return (idx + 1) % n; } int solve(int begin, int end, const vector<int> &A) { if (next(begin) == end) return 0; if (dp[begin][end]) return dp[begin][end]; int best = INT_MAX; for (int i = next(begin); i != end; i = next(i)) best = min(best, A[begin]*A[i]*A[end] + solve(begin, i, A) + solve(i, end, A)); dp[begin][end] = best; return best; } int minScoreTriangulation(vector<int>& A) { n = A.size(); dp.resize(n, vector<int>(n)); int best = INT_MAX; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) best = min(best, solve(i, j, A) + solve(j, k, A) + solve(k, i, A) + A[i] * A[j] * A[k]); return best; }
weekly 136
(dp) 1043. Partition Array for Maximum Sum
Example
Input: A = [1,15,7,9,2,5,10], K = 3 Output: 84 Explanation: A becomes [15,15,15,9,10,10,10]
Return the largest sum of the given array after partitioning.
int maxSumAfterPartitioning(vector<int>& A, int K) { // From lee215: // dp[i] record the maximum sum we can get considering A[0] ~ A[i] // // To get dp[i], we will try to change k last numbers separately to // the maximum of them, where k = 1 to k = K. const int n = A.size(); int dp[n]; dp[0] = A[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { int maxSum = 0; int maxElem = 0; for (int j = 0; j < K; ++j) { if (i - j < 0) continue; maxElem = max(maxElem, A[i - j]); int curSum = maxElem * (j + 1); if (i - j - 1 >= 0) curSum += dp[i - j - 1]; maxSum = max(maxSum, curSum); } dp[i] = maxSum; } return dp[n - 1]; }
// By neal_wu's contest solution int maxSumAfterPartitioning(vector<int>& A, int K) { int N = A.size(); vector<int> dp(N + 1, 0); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { int most = 0; for (int j = i - 1; j >= max(i - K, 0); j--) { most = max(most, A[j]); dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + (i - j) * most); } } return dp[N]; }
No comments:
Post a Comment